SemiPar.depCens : A new package for fitting the Cox proportional hazards model under dependent censoring
SemiPar.depCens
In this post, I will discuss the SemiPar.depCens package and its usage in practical applications. The SemiPar.depCens package is built to provide easy-to-use functions in R for estimation of the dependent censoring methodology proposed in Deresa and Van Keilegom (2024). The approach presented in the latter paper is based on a parametric copula for the relation between the survival time and the censoring time, and the parameter defining the copula does not need to be known. Instead, the copula parameter is estimated jointly with other finite model parameters by following a pseudo-likelihood approach. The main idea is to decompose the estimation in two steps instead of a direct optimization. First, obtain a consistent estimator of the cumulative hazard function using a martingale-based estimating equation. Then, substitute it into the likelihood function to obtain the pseudo maximum likelihood estimator for finite-dimensional parameters. This allows us to overcome a very complex estimation of the Cox model due to the presence of dependent censoring.
Available copula functions in SemiPar.depCens package includes Frank, Gumbel and Normal copulas. Only Weibull and Lognormal models are allowed for the censoring model, even though any parametric model that satisfies certain identifiability conditions could be used.
Installation
The SemiPar.depCens package is available here on the CRAN and can be installed for free. To install it in R, use:
install.packages("SemiPar.depCens")
Example
This is a basic example which shows how to use the package in practice.
library(SemiPar.depCens)
data("follic") # load the data
# Prepare the data in the way that is used by the package
follic = follic[order(follic$time),] # order the observed survival time
Z = round(follic$time,digits = 3)
d1 = as.numeric(follic$status==1) # censoring indicator for survival time T
d2 = as.numeric(follic$status==2) # censoring indicator for dependent censoring C
treat = as.numeric(follic$ch=="Y") # treatment indicator
age = (follic$age-mean(follic$age))/sd(follic$age) # recommended to standardize continuous variables
hgb = (follic$hgb-mean(follic$hgb))/sd(follic$hgb) # standardized hemoglobin
clinstg = as.numeric(follic$clinstg==1) # clinical stage
X = cbind(treat,age,hgb,clinstg) # data matrix for T, should be in matrix form
W = cbind(rep(1,length(Z)),treat,age,hgb,clinstg) # data matrix for C, should be in matrix form
resData = data.frame("Z" = Z,"d1" = d1, "d2" = d2) # resData should be a data frame
Fit dependent censoring model
The following code fit a default copula, which is Frank, for the relation between the survival time (T) and dependent censoring time (C). The default marginal model for C is a Weibull model. Other capabilities can be explored by typing ?fitDepCens in the console.
fitD <- fitDepCens(resData = resData, X = X, W = W, bootstrap = FALSE)
The output for the above code chunk should look as below. Since bootstrapping = FALSE, it does not make any inference based on p-values; only parameter estimates are shown.
summary(fitD)
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Summary of dependent censoring model
##
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
##
## Survival submodel: Cox proportional hazards model
##
## Parameter estimates:
## treat age hgb clinstg
## -0.347 0.352 0.042 -0.646
##
## Censoring submodel: Weibull
##
## Intercept treat age hgb clinstg sigma
## 2.803 0.125 -0.658 -0.038 0.411 0.618
##
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
##
## Assumed copula model: Frank
##
## Association parameter
## tau
## 0.336
We can do bootstrapping by setting bootstrap = TRUE, but note that the algorithm may take long time to finish the computations, even after parallelization is used to speed up the work. The default number of bootstrap size is 50. Increasing number of bootstrap samples may produce more precise standard error estimates.
fitD <- fitDepCens(resData = resData,X = X, W = W, bootstrap = TRUE, n.boot = 50)
summary(fitD)
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Summary of dependent censoring model
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
##
## Survival submodel: Cox proportional hazards model
##
## Estimate Boot.SE Pvalue
## treat -0.347 0.161 0.031
## age 0.352 0.062 0.000
## hgb 0.042 0.056 0.449
## clinstg -0.646 0.122 0.000
##
## Censoring submodel: Weibull
##
## Estimate Boot.SE Pvalue
## Intercept 2.803 0.118 0.000
## treat 0.125 0.164 0.445
## age -0.658 0.087 0.000
## hgb -0.038 0.081 0.639
## clinstg 0.411 0.135 0.002
## sigma 0.618 0.051 0.000
##
## Assumed copula model : Frank
##
## Association parameter
## tau Boot.SE Pvalue
## 0.336 0.094 0.000
Fit independent censoring model
For independent censoring model, the assumption is that the copula parameter between T and C is zero. Hence, the model is very simplified in terms of computational costs. We obtain results very quickly in comparison to dependent censoring model. The default model for censoring distribution is Weibull.
fitI<- fitIndepCens(resData = resData, X = X, W = W, bootstrap = TRUE, n.boot = 50)
summary(fitI)
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Summary of independent censoring model
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
##
## Survival submodel: Cox proportional hazards model
##
## Estimate Boot.SE Pvalue
## treat -0.365 0.158 0.021
## age 0.329 0.061 0.000
## hgb 0.041 0.081 0.609
## clinstg -0.648 0.136 0.000
##
## Censoring submodel: Weibull
##
## Estimate Boot.SE Pvalue
## Intercept 3.208 0.168 0.000
## treat 0.127 0.243 0.602
## age -0.703 0.087 0.000
## hgb -0.029 0.103 0.779
## clinstg 0.333 0.166 0.046
## sigma 0.608 0.049 0.000
Cumulative hazard function
Let us compare the estimated cumulative hazards based on the two fitted models.
plot(fitD$observedTime, fitD$cumhazardFunction, type = "l",xlab = "Time",
ylab = "Cumulative hazard function", cex = 1.5, lwd = 1.5)
lines(fitI$observedTime, fitI$cumhazardFunctio, col = "red", lty = 1, lwd = 1.5, cex = 1.5)
legend(8, 0.85, legend = c("Dependent censoring model", "Independent censoring model"),
lty = c(1,1,1), col = c("black", "red"), cex = 1.2, bty = "n")
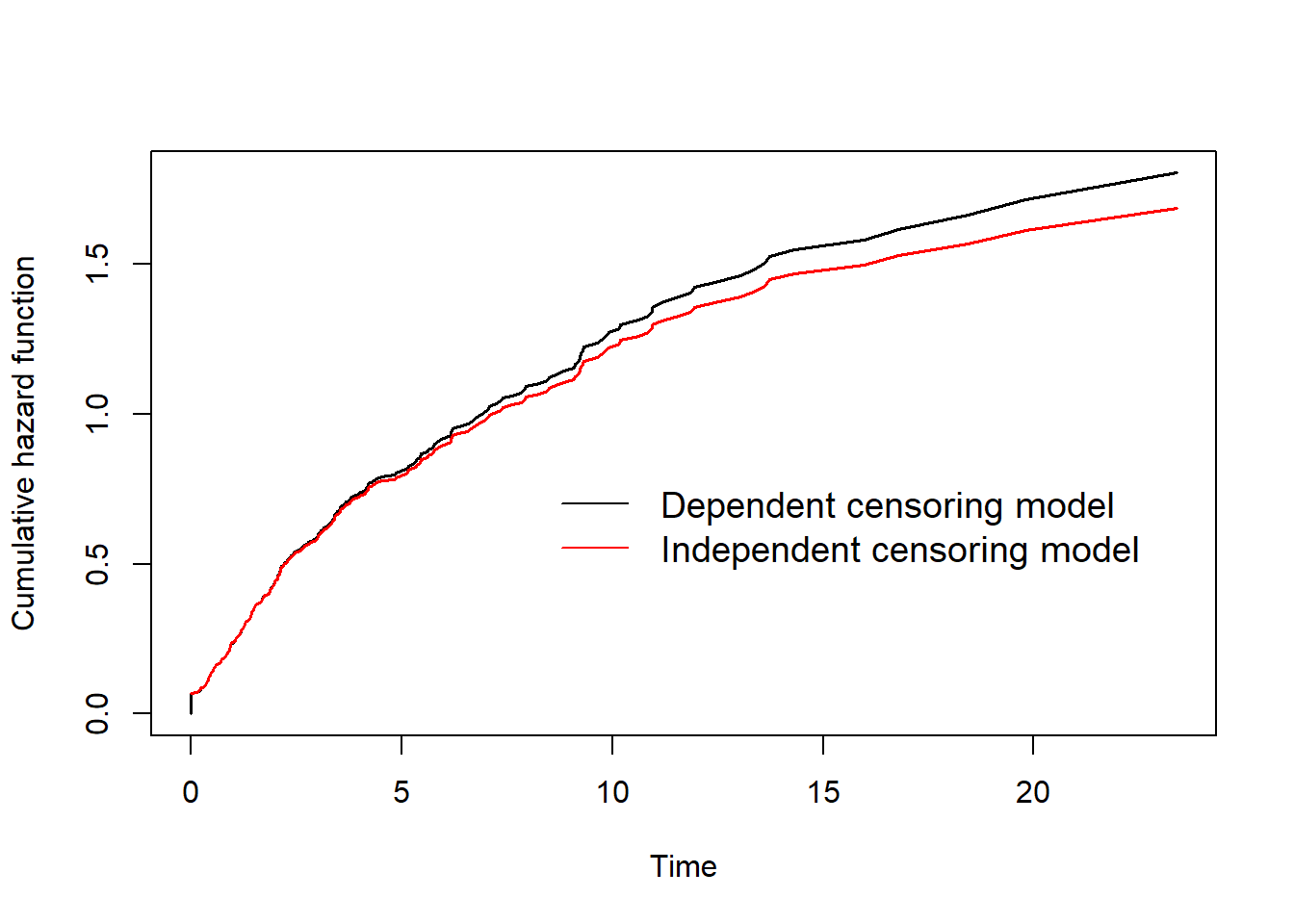 This figure shows that the estimated cumulative hazard curve based on the independent censoring model underestimates the one based on the dependent censoring model. This is in agreement with our expectation given that the association between the time to relapse and death is positive. Similar phenomena were observed when using the survival functions to compare the two models instead of cumulative hazards (see my previous post for more details on this topic).
This figure shows that the estimated cumulative hazard curve based on the independent censoring model underestimates the one based on the dependent censoring model. This is in agreement with our expectation given that the association between the time to relapse and death is positive. Similar phenomena were observed when using the survival functions to compare the two models instead of cumulative hazards (see my previous post for more details on this topic).